Meat is a primary source of protein in human diets, essential for health and development. However, the traditional meat industry faces significant challenges, including environmental degradation, ethical concerns, and health risks. Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured or cell-based meat, offers a sustainable and ethical alternative. Produced by cultivating animal cells in a controlled environment, it eliminates the need for animal slaughter while reducing the environmental footprint associated with traditional livestock farming.
This blog delves into the technology behind lab-grown meat, exploring its production process, benefits, and challenges. From reducing greenhouse gas emissions to addressing animal welfare concerns, lab-grown meat has the potential to revolutionize the global food industry. As the world grapples with a climate crisis and growing health issues, lab-grown meat emerges as a promising solution for a more sustainable and ethical future.
Signicent has extensive experience in Patent Landscape Services, helping companies analyze trends, identify competitors, and uncover opportunities in the lab-grown meat industry.
Is Lab-Grown Meat More Sustainable and Safer to Consume?
The Sustainability Edge
Lab-grown meat is more sustainable than traditional meat for several reasons:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Traditional livestock farming contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. Lab-grown meat requires fewer resources like land, water, and feed.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Studies show lab-grown meat could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 78% compared to conventional meat.
- Animal Welfare: Lab-grown meat eliminates the need for animal slaughter, addressing ethical concerns.
Safety and Health Benefits
- Controlled Production: Lab-grown meat is produced in sterile conditions, reducing the risk of contamination by pathogens like E. coli and Salmonella.
- Customizable Nutrition: Scientists can adjust the nutritional profile of lab-grown meat, potentially reducing unhealthy fats and enhancing beneficial nutrients.
- No Antibiotics: Lab-grown meat production doesn’t require antibiotics, reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Lab-Grown Meat vs. Traditional Meat: A Comparative Analysis
| Aspect | Lab-Grown Meat | Traditional Meat |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, minimal resource use | High carbon footprint, resource-intensive |
| Animal Welfare | No animal slaughter required | Involves animal slaughter |
| Production Time | Weeks | Months to years |
| Nutrition | Customizable, potentially healthier | Fixed nutritional profile |
| Cost | Currently high, but expected to decrease | Relatively low |
| Consumer Acceptance | Growing but still limited | Widely accepted |
Signicent conducts Chemical Structure Searches to identify patented compounds, helping companies innovate safely in the lab-grown meat sector.
Current Challenges Driving Research in Lab-Grown Meat
Lab-grown meat is being developed as a solution to several pressing global challenges. Researchers are working on this innovative technology to address issues like fungal viruses, health risks, and environmental degradation caused by traditional meat production. Below are the key challenges driving the development of lab-grown meat:
1. Fungal and Viral Infections in Animals
Animals like chickens and livestock are prone to fungal and viral infections, which can spread to humans through meat consumption, posing serious health risks and outbreaks.
2. Health Risks from Traditional Meat Consumption
Consuming traditional meat has been linked to cardiovascular diseases, antibiotic resistance, and other health issues, raising concerns about long-term human health and well-being.
3. Environmental Degradation
Traditional livestock farming contributes to deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and water pollution, putting immense pressure on the planet’s natural resources and ecosystems.
4. Animal Welfare Concerns
Factory farming raises ethical concerns about animal treatment, including overcrowding, inhumane conditions, and the slaughter of billions of animals annually, sparking global outrage.
5. Antibiotic Resistance
Livestock farming relies heavily on antibiotics, contributing to the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which poses a significant threat to global health and medical treatments.
Signicent’s Technology Scouting identifies emerging technologies in lab-grown meat, helping businesses stay ahead of the competition.
The Making of Lab-Grown Meat: A Step-by-Step Visual Explanation
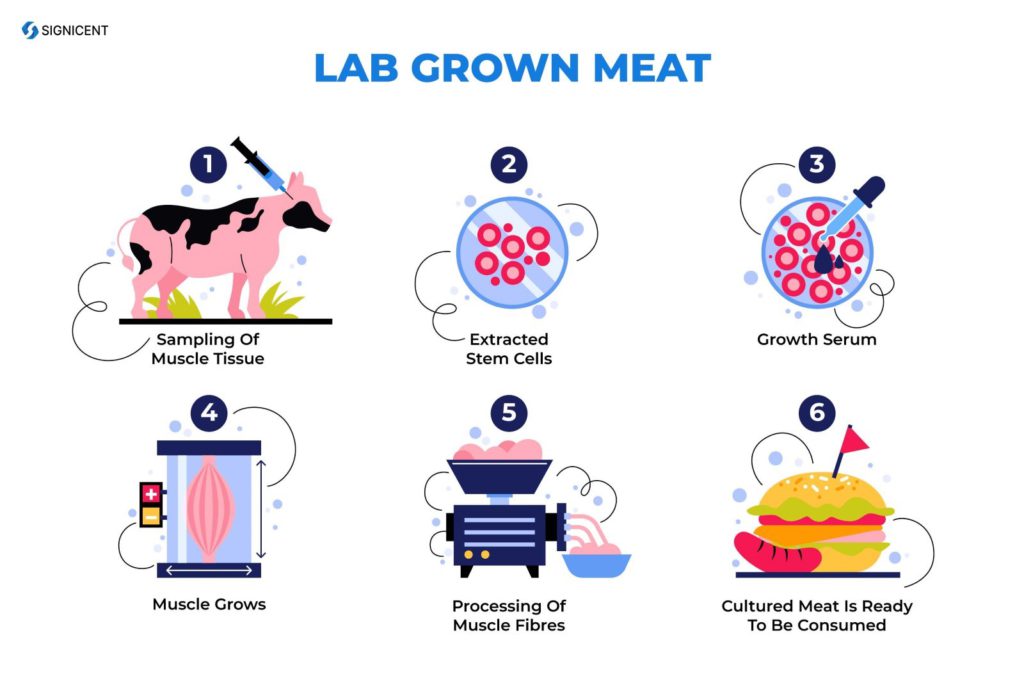
How Lab-Grown Meat is Made: A Step-by-Step Guide
Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured or cell-based meat, is a revolutionary innovation in the food industry. It offers a sustainable and ethical alternative to traditional meat production by growing animal cells in a controlled environment. Below is a detailed, step-by-step explanation of how lab-grown meat is made, from cell extraction to the final product ready for consumption.
1. Cell Extraction
The process begins with the extraction of stem cells from a live animal. These cells are typically taken from muscle tissue, as they have the unique ability to differentiate into various types of cells, including muscle and fat cells, which are essential for creating meat.
- Why Stem Cells? Stem cells are chosen because they can self-renew and transform into specialized cells, making them ideal for growing meat in a lab.
- Animal Welfare: The extraction process is minimally invasive and does not harm the animal, addressing ethical concerns associated with traditional meat production.
2. Cell Line Establishment
Once extracted, the stem cells are placed in a nutrient-rich medium that provides the necessary nutrients, vitamins, and growth factors for the cells to multiply.
- Nutrient Medium: This medium often includes amino acids, sugars, and proteins to support cell growth.
- Cell Multiplication: Over time, the cells multiply and form a stable cell line, ensuring a consistent supply of cells for meat production.
3. Cell Culture
The cells are then transfer to a bioreactor, a controlled environment that mimics the conditions inside an animal’s body.
- Bioreactor Function: The bioreactor provides the ideal temperature, oxygen levels, and nutrient supply for the cells to grow and differentiate into muscle and fat tissues.
- Scaling Up: Bioreactors can range in size, from small lab-scale units to large industrial systems designed for mass production.
- Differentiation: During this stage, the cells differentiate into muscle fibers and fat cells, which are the building blocks of meat.
4. Scaffolding
To give the meat its structure, scientists use edible scaffolds. These scaffolds act as a framework, helping the cells organize into a three-dimensional form that resembles traditional meat.
- Types of Scaffolds: Scaffolds can be make from plant-based materials or biodegradable polymers.
- Texture and Structure: The scaffolds play a crucial role in replicating the texture and structure of conventional meat, ensuring a familiar eating experience.
- Innovation: Advances in scaffolding technology are helping to create more complex meat products, such as steaks and chicken breasts, rather than just ground meat.
5. Harvesting and Processing
Once the cells have matured and formed muscle and fat tissues, the meat is harvest and processed.
- Harvesting: The lab-grown meat is carefully removed from the bioreactor and scaffolds.
- Processing: The meat is then cleaned, shaped, and prepared for consumption. It can be ground into patties, shaped into nuggets, or even formed into more complex cuts.
- Final Product: The end result is a product that looks, cooks, and tastes like traditional meat but is produced in a more sustainable and ethical way.
6. Cooking and Consumption
Lab-grown meat can be used in the same way as traditional meat. It can be cooked, seasoned, and incorporated into a wide range of dishes, from burgers to stir-fries.
- Cooking Methods: Lab-grown meat can be grilled, fried, baked, or sautéed, just like conventional meat.
- Nutritional Profile: Scientists can customize the nutritional content of lab-grown meat, making it potentially healthier by reducing saturated fats and increasing beneficial nutrients.
- Consumer Acceptance: While lab-grown meat is still gaining acceptance, its similarity to traditional meat in taste and texture is helping to win over consumers.
Signicent’s Biological Sequence Search identifies patented biological materials, helping businesses develop lab-grown meat products without legal risks.
New-Age Solutions to Overcome Challenges
- Stem Cell Technology
Research in stem cells is improving how cells grow and develop, making meat production faster and more affordable. Scientists are working on better cell lines that need fewer resources while keeping the meat’s nutrition and texture intact.
- Bioreactor Innovations
New bioreactors are being design to handle larger production, monitor conditions automatically, and create stable growth environments. These improvements help lower costs, reduce contamination risks, and make lab-grown meat easier to produce at scale.
- AI and Automation
Artificial intelligence helps track and adjust cell growth in real time, ensuring stable production. AI improves efficiency by managing nutrients, monitoring cell health, and maintaining consistency, which helps lower costs.
- Consumer Education
Many people are unfamiliar with lab-grown meat. Clear information about its safety, sustainability, and benefits—supported by regulatory approvals—can help build trust and increase acceptance in the market.
Signicent’s FTO Search Services provide comprehensive patent risk assessments, ensuring companies can safely bring lab-grown meat products to market.
Benefits of Lab-Grown Meat from a Sustainability Perspective
Resource Efficiency
- Lab-grown meat requires less land, water and feed compared to traditional livestock farming, reducing strain on natural resources and promoting efficient resource use.
Reduced Emissions
- It significantly lowers greenhouse gas emissions, contributing less to climate change and helping combat global warming more effectively than conventional meat production.
Biodiversity Preservation
- By reducing the need for deforestation and habitat destruction, lab-grown meat helps protect ecosystems and preserve biodiversity for future generations.
Ethical Production
- Lab-grown meat eliminates the need for animal slaughter, offering a cruelty-free alternative that aligns with ethical and humane treatment of animals.
Signicent’s Market Intelligence services provide insights into consumer trends, helping businesses tailor their lab-grown meat products to meet market demands.
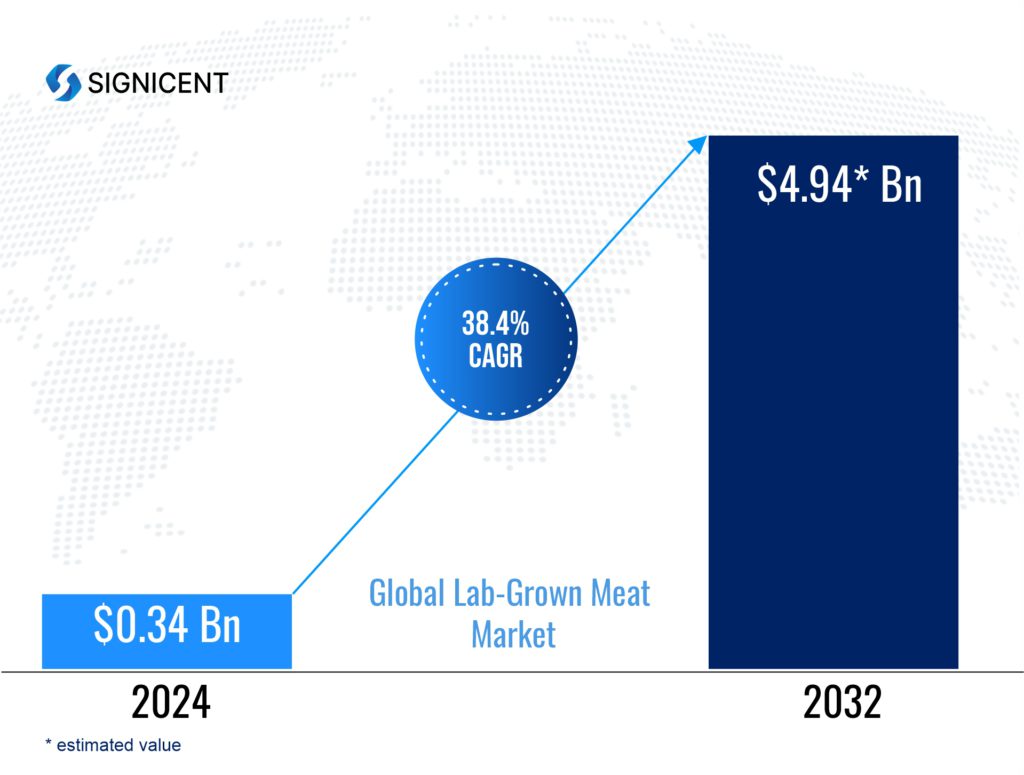
Market intelligence
The global lab-grown meat market is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years. According to Signicent Market Research reports, the market is projected to reach significant values by 2032, driven by advancements in cellular agriculture, increasing demand for sustainable protein sources, and growing consumer awareness of alternative meat options.
Through Competitive Intelligence, Signicent helps companies understand their competitors’ strategies and position themselves effectively in the lab-grown meat market.
Here are seven leading players in the lab-grown meat industry:

Signicent helped companies in the lab-grown meat industry with technology scouting, patent research, and market analysis. We identified advancements in stem cell technology, bioreactor systems, and AI applications, helping businesses improve production efficiency and reduce costs.
Through regulatory research and market insights, we assisted companies in understanding approval processes and finding market opportunities. Our work also included evaluating protein alternatives, improving supply chains, and tracking industry developments to keep businesses competitive.
If you are working on such technological solutions and need industry insights, you can contact us. We provide services in White Space Analysis and Technology Gaps. We also offer research support through problem-solution approaches.
Conclusion
Lab-grown meat signifies a significant shift in protein production and consumption. By utilizing innovative technologies, it addresses key environmental, ethical, and health issues associated with traditional meat production. Although the industry faces challenges like as high prices and scalability, continued research and increased consumer awareness are pushing growth. Lab-grown meat has the potential to transform the global food system by providing a cleaner, safer, and more sustainable alternative to traditional meat, clearing the path for a more promising future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Lab-Grown Meat
1. What is lab-grown meat?
Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured or cell-based meat, offers a sustainable and ethical alternative.
2. Is lab-grown meat safe to eat?
Yes, it is produce in sterile conditions, reducing contamination risks and ensuring a safer product compared to conventional meat.
3. How does lab-grown meat help the environment?
It uses less land, water, and feed, and significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional livestock farming.
4. Does lab-grown meat taste like traditional meat?
Yes, it is design to replicate the taste, texture, and nutritional profile of conventional meat for a similar experience.
5. When will lab-grown meat be widely available?
It is already available in limited markets, but global availability depends on cost reductions, scaling production, and regulatory approvals.
About Signicent LLP
We assist businesses globally in their technology innovations, R&D, new product development, patents, valuation, product commercialization & market research needs.
Services Offered:
- Patent Landscape
- Patent Portfolio Analysis
- Patent Invalidity Search
- Patent Licensing Services
- Freedom to operate (FTO)
- Chemical Structure Search
- Design Patent Search
- Technology Scouting
- Technology Landscape Analysis
- Technology gap analysis
- Technology Intelligence
- Market Research
- Bio Sequence Search
- Manufacturers Search/ Supplier search
Elevate your Innovation and Research with Signicent’s cutting edge approach to assist you with Technology and Market related matters alongside the IP aspect of the analysis.


