Introduction – From Rooftops to Transparent Windows
Solar technology has moved far beyond rooftop installations. Today, buildings need energy systems that are efficient, aesthetic, and integrated – not bulky structures that compete for space. However, traditional solar panels still face limitations in design flexibility and available surface area, especially in dense urban environments.
Buildings today consume massive amounts of energy, but most surfaces remain idle. To address this limitation, engineers and architects are pursuing solutions that combine performance and design. Transparent solar panels exemplify this transformation, converting glass from a passive element to an active energy generator that absorbs sunlight while maintaining visibility.
As cities grow taller and electricity demand increases, this approach is becoming essential. Moreover, transparent solar panels align with smart-building goals, circular material use, and net-zero regulations. As a result, they offer a future where structures do more than consume energy; they actively contribute to clean power generation.
A structured current & future analysis helps identify global adoption of hotspots, regional installation behavior, and how transparent solar solutions scale across markets.
How solar panels generate electricity
At its simplest, a solar panel converts sunlight into electricity using semiconductor materials such as silicon. When photons strike the material, they free electrons that flow through a circuit—generating direct current (DC).
Traditional panels rely on monocrystalline or polycrystalline silicon, offering 15–22 % efficiency. However, material purity and heat losses restrict further gains.
To break this ceiling, scientists are moving toward multi-junction cells and perovskite-based hybrids, which harvest a broader range of the solar spectrum.
What are transparent solar panels
Transparent solar panels are photovoltaic systems designed to generate electricity while allowing visible light to pass through. Unlike traditional solar panels that absorb most of the sunlight and appear opaque, these panels selectively capture specific wavelengths, typically ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR)—while remaining visually transparent.
From an engineering perspective, this is achieved through advanced materials such as transparent conductive oxides, organic photovoltaics, or quantum-dot-based coatings. These materials enable power generation without blocking the view or altering architectural aesthetics.
In simple terms:
they look like glass, function like solar panels, and integrate directly into buildings.
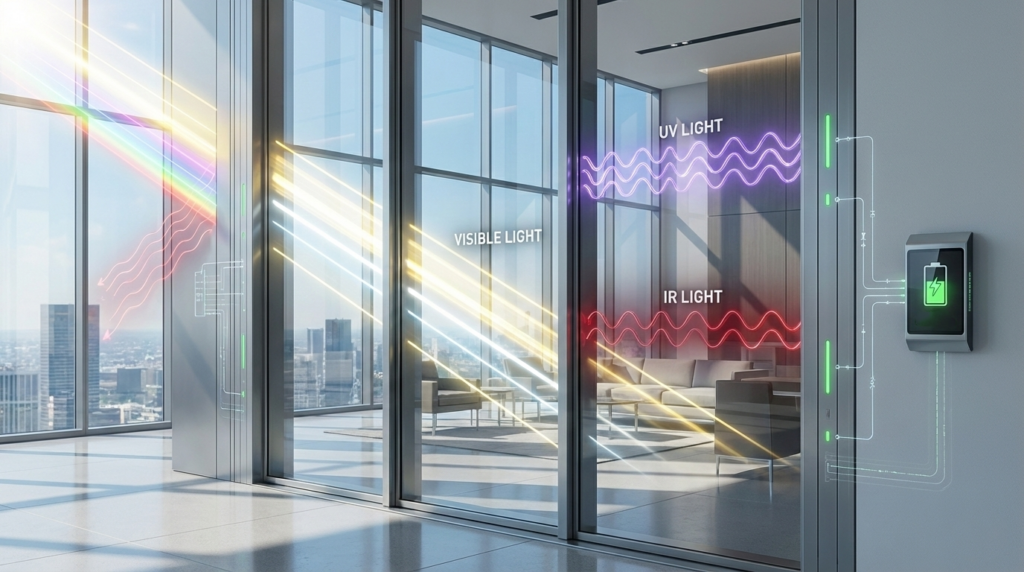

How Transparent Solar Panels Work
The working principle of transparent solar panels is based on selective light harvesting.
Sunlight contains multiple wavelengths:
- Visible light (what we see)
- Ultraviolet light
- Infrared light
Transparent solar panels are engineered to:
- Allow visible light to pass through
- Capture UV and IR light
- Convert the captured energy into electricity via photovoltaic processes
The generated electricity is then routed through embedded wiring to inverters and building energy systems, just like conventional solar installations.
From a system-design standpoint, this enables integration into:
- Windows
- Facades
- Skylights
- Curtain walls
- Glass roofs
The key challenge engineers solve here is balancing transparency, efficiency, and durability—and that balance is improving with each generation of technology.
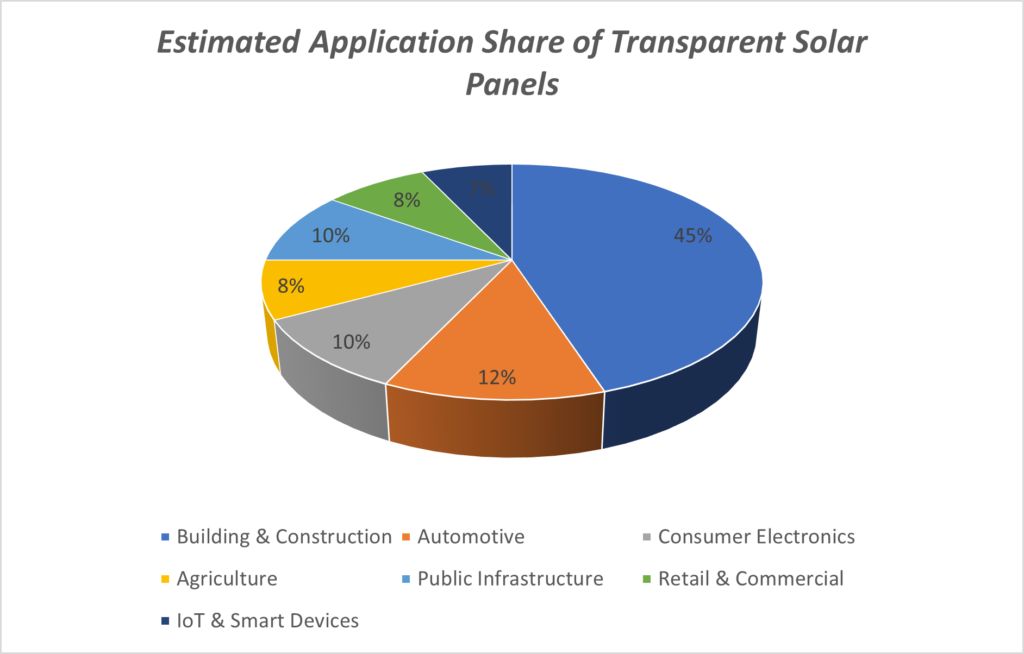
According to the pie chart, transparent solar panels are spreading across diverse ecosystems, covering buildings, vehicles, electronics, agriculture, public infrastructure, retail environments, and smart IoT systems, enabling energy generation beyond rooftops.
Why Today’s Solar Systems Need a Modern Upgrade
Silicon solar cells have changed the way we get energy, yet they still have several problems:
- Efficiency plateau: Commercial cells rarely exceed 23%.
- Energy-intensive manufacturing: Silicon refining demands high temperatures and toxic chemicals.
- End-of-life waste: Millions of panels will reach disposal age by 2035.
- Land and space demands: Large solar farms require vast land footprints.
The sustainability paradox is clear renewable doesn’t always mean responsible unless the full life cycle is optimized.
Why Transparent Solar Panels Are Needed Today
Modern cities face a unique energy paradox. Buildings consume massive amounts of power, yet available surface area for energy generation is limited.
Traditional rooftop solar works well, but only up to a point.
Transparent solar panels address several present-day challenges:
- Urban density limits roof availability
- Glass-dominated architecture increases energy loss
- Sustainability mandates demand on-site renewable generation
- Net-zero building goals require integrated solutions
Instead of competing for space, transparent solar panels use surfaces that already exist. This makes them especially valuable in commercial real estate, smart cities, and infrastructure-heavy environments.
Urban buildings are running out of rooftop space for solar installations, and as glass usage in modern architecture continues to increase, Technology Monitoring becomes essential to track how these new materials perform. Integrating energy generation directly into windows offers a practical solution for dense cities, enabling real-time observation of efficiency, durability, and sustainability in future urban environments.
Top 5 Factors: Traditional vs Transparent Solar
| Factor | Traditional Solar | Transparent Solar |
| 1. Space Requirement | Needs dedicated rooftops or land space | Converts existing glass/windows into power-generating surfaces |
| 2. Aesthetics & Architecture | Bulky, dark panels disrupt building design | Nearly invisible, blends into modern architecture |
| 3. Installation Flexibility | Limited to open sunlight and tilt-based mounting | Works on façades, windows, vehicles, skylights — vertical surfaces usable |
| 4. Light Utilization | Depends mainly on direct visible sunlight | Captures UV/IR wavelengths, lets visible light pass through |
| 5. Use-Case Expansion | Mostly for power plants & rooftop residential | Enables urban, automotive, mobile, and building-integrated PV adoption |
| 6. Sustainability | More materials, higher waste load | Thin-film layers, lower material use and footprint |
| 7. Heat / Energy Behavior | Gets hot and loses efficiency | Operates cooler, maintains more stable output |
Key Innovations & Patented Breakthroughs
Cutting-edge R&D is redefining what solar panels can do. Here are four innovations leading the change:
- Perovskite–Silicon Tandem Cells (Oxford PV, UK)
Patented multi-junction architecture surpassing 33 % efficiency, integrating low-cost perovskite layers atop silicon wafers.
- Transparent Photovoltaics (Ubiquitous Energy, USA)
Invisible solar coatings for windows and façades that generate power without compromising aesthetics.
- Solar Skins & Building-Integrated PV (Tesla & Onyx Solar)
Customizable solar surfaces that blend with architecture—roofs, walls, and even roads—turning infrastructure into active energy assets.
- Recyclable Thin-Film Panels (First Solar & Helia Tek)
Employing cadmium-telluride and organic polymers for flexible, lightweight modules; 95 % recyclable by mass.
These patents mark a decisive move from hardware-centric panels to smart, integrated solar ecosystems.
Recent advancements in material science have significantly improved transparency and durability. In addition, IoT-enabled monitoring systems allow real-time performance tracking. As a result, transparent solar panels are becoming smarter, not just cleaner.
The Role of Emerging Technologies
New-age solar isn’t limited to materials—it’s about intelligence and adaptability.
- AI & Machine Learning: Predict sunlight variability, optimize, tracking angles, and forecast maintenance using predictive analytics.
- IoT Connectivity: Each panel node communicates performance data to a central system, enabling real-time energy management.
- Automation in Manufacturing: Robotic laser patterning reduces defects, ensuring consistency in perovskite layer deposition.
- 3D Printing & Nano-Manufacturing: Custom solar geometries and printed circuits for wearables and curved surfaces.
- 6G & Smart Grids: Integrating solar micro-plants with ultra-fast data transfer for decentralized, autonomous power distribution.
Together, these technologies transform panels from passive collectors into intelligent energy systems.
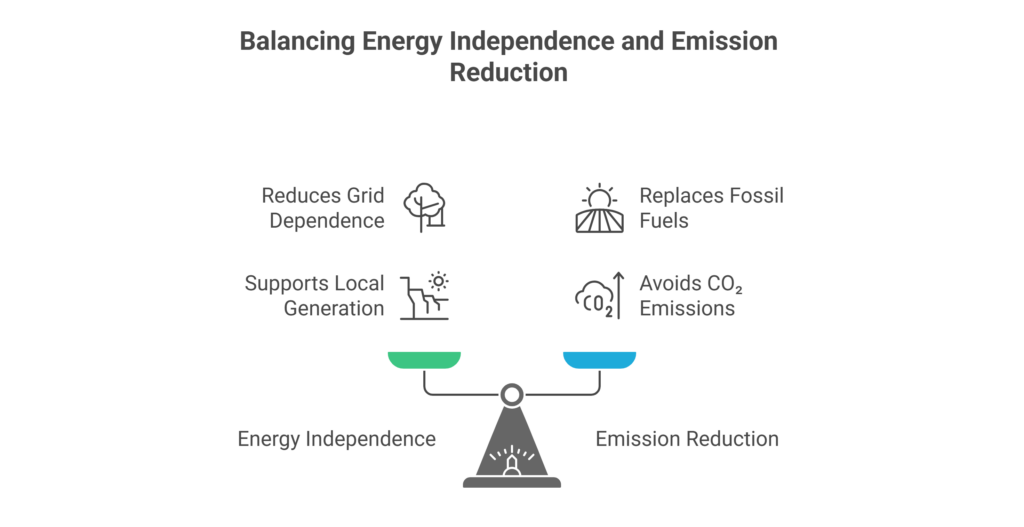
Top 5 Benefits & Sustainability Highlights
- Dual-Purpose Infrastructure: Converts windows into energy assets, generating electricity without occupying rooftops or altering building geometry.
- Architectural Freedom: Maintains daylight visibility while harvesting UV/IR energy, enabling renewable adoption without aesthetic disruption.
- Energy Independence: Reduces purchased grid electricity during peak demand, supporting localised renewable generation and lower operational strain.
- Emission Reduction: Replaces fossil-based electricity and avoids roughly nine hundred grams of CO₂ per kilowatt-hour generated.
- Urban Sustainability: Generates electricity using vertical glass structures, reducing land pressure and supporting dense smart-city development.
Global Market Outlook
The global solar landscape is rapidly transitioning toward integrated energy-harvesting surfaces, driven by architectural electrification, urban densification, and decentralised clean energy adoption.
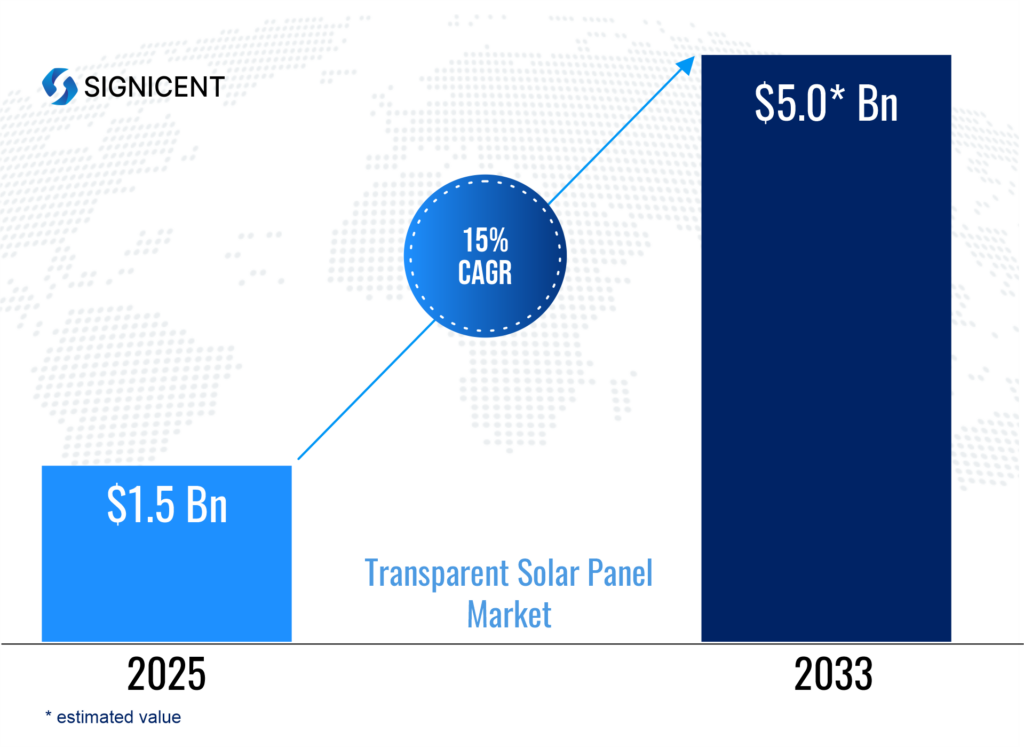
According to Signicent Market Research, the global transparent solar panel market is projected to rise from USD 1.5 Bn in 2025 to USD 5.0 Bn by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 15%.
Why Markets Are Adopting Transparent Solar Faster
Growing adoption is coming from regions pushing urban sustainability, façade electrification, and net-zero mandates:
- United States – commercial smart buildings, EV integration, and university-led perovskite pilots.
- Japan & South Korea – transparent PV for smart cities, automotive glass, and infrastructure electrification.
- Germany & Netherlands – agrivoltaics, green buildings, and clean façade retrofits across dense urban spaces.
Key Emerging Players
A new tier of innovators is scaling thin-film, OPV, and perovskite architectures into mainstream production:
- First Solar (USA) – scaling thin-film PV with circular recycling loops.
- LONGi (China) – advancing high-efficiency heterojunction and tandem module manufacturing.
- Oxford PV (UK) – commercial perovskite-silicon tandem cell breakthroughs.
- Heliatek (Germany) – lightweight OPV films for mobility and structural integration.
- Adani Solar (India) – driving cost-effective PV manufacturing and large-scale deployment.
- Next Energy (Japan) – urban rollout of transparent PV for building retrofits.
Top 5 Startups to Watch
Startups are merging design, thin-film chemistry, and invisible PV integration:
- SolarSkin Tech – architectural solar skins for design-centric facades.
- Transparent PV Labs – UV/IR harvesting coatings for windows and glass.
- Solivus (UK) – lightweight curved PV for urban rooftops and stadiums.
- Ubiquitous Energy (USA) – fully transparent photovoltaic window glass.
- Brite Solar (Greece) – transparent agrivoltaics for greenhouses and crop facilities.
At Signicent, we help energy pioneers translate laboratory breakthroughs into global market success through:
- Patent Landscape Analysis: Tracking global IP in perovskite cells, transparent PV, and recycling technologies.
- Market Research: Quantifying opportunities across rooftop, BIPV, and microgrid sectors.
- Technology Scouting: Identifying material suppliers, R&D partners, and academic collaborations.
- Competitor Benchmarking: Evaluating efficiency metrics, cost trends, and commercialisation timelines.
- Sustainability & Life-Cycle Assessment: Supporting ESG reporting and green-tech certification readiness.
Our expertise ensures innovators stay ahead in an industry defined by rapid technological leaps and tight regulatory frameworks.
Conclusion – Lighting the Path to a Solar Civilization
The future of solar is not a technology race, but rather a human shift. It is about providing better air in cities, lower energy bills for families, and reliable power to communities without losing space, design, or comfort. Transparent solar transforms everyday surfaces—windows, façades, and screens—into silent energy helpers, making sustainability feel effortless rather than manufactured. As sunshine becomes something we live with rather than chase from a rooftop, renewable energy ceases to be an afterthought and becomes an integral part of existence.
What comes next isn’t simply efficiency; it’s freedom: freedom from fossil fuels, absolute for architects to create, and opportunity for emerging economies to grow without pollution. And when scholars, politicians, and industry partners work with innovation teams, that future comes sooner.
Transparent solar panels represent a shift in how we think about renewable energy. Instead of adding panels to buildings, energy generation becomes part of the building itself. Over time, this approach will redefine sustainable design across cities worldwide.
FAQs on Transparent Solar Panels
As solar glass evolves, people increasingly ask how transparent panels function, where they fit, and what real-world performance benefits they deliver.
How do transparent solar panels generate electricity?
They capture UV/IR wavelengths through special materials and convert that energy into usable electrical power.
Are transparent solar panels durable outdoors?
Yes, commercial products are built with weather-resistant coatings and are designed for long-term exterior exposure.
Can transparent solar panels power an entire building?
They assist with daytime electricity loads, but full independence usually requires storage or additional solar sources.
Do transparent solar panels affect visibility through windows?
Most designs maintain clear visibility, allowing daylight to pass through without major visual distortion.
Are transparent solar panels expensive to install?
Costs remain higher than standard panels, but prices are falling as scaling and manufacturing improve.
What materials are used in transparent solar panels?
They commonly use organic PV, perovskites, or dye-sensitized cells designed to absorb non-visible light bands.
About Signicent LLP
We assist businesses globally in their technology innovations, R&D, new product development, patents, valuation, product commercialization & market research needs.
Services Offered:
- Patent Landscape
- Patent Portfolio Analysis
- Patent Invalidity Search
- Patent Licensing Services
- Freedom to operate (FTO)
- Chemical Structure Search
- Design Patent Search
- Technology Scouting
- Technology Landscape Analysis
- Technology gap analysis
- Technology Intelligence
- Market Research
- Bio Sequence Search
Elevate your Innovation and Research with Signicent’s cutting-edge approach to assist you with Technology and Market related matters alongside the IP aspect of the analysis.


