In an era where sustainability is a global priority, the reduction of carbon emissions stands out as a crucial goal. This focus is leading to groundbreaking advancements and a renewed commitment to protecting our environment. Hydrogen, especially green hydrogen, is gaining traction as a crucial energy source. Countries like Germany, the United States, and Japan are pioneering the use of hydrogen, with a focus on blue and green variants, particularly in the automotive sector.
Dutch companies are currently investing in developing green hydrogen in countries where green power, needed to produce green hydrogen, can be easily generated, such as Namibia and Brazil. As per SciTech daily, EU aims to produce 10 million tones of green hydrogen by 2030. By 2030, the EU aims to have a significant portion of new vehicles powered by hydrogen, emphasizing its importance in combating climate change.
The automotive industry, facing the need to cut emissions and improve energy efficiency, views hydrogen as a solution. Europe has emerged as a global leader in the pursuit of clean energy solutions, and green hydrogen is at the forefront of its efforts to decarbonize its economy. With its ambitious climate goals and supportive policies, Europe is driving significant advancements in hydrogen production, storage, and utilization.
Signicent helps companies identify patent trends in the green hydrogen sector through Patent Landscape Services, aiding strategic decision-making and fostering innovation to accelerate sustainable hydrogen technologies.
Types of Hydrogen and their future impact
Hydrogen is classified into grey, blue, and green types, each with different environmental impacts based on production methods.
- Grey Hydrogen: Produced from natural gas via steam methane reforming (SMR), grey hydrogen is the most common but releases large amounts of CO2, making it unsustainable in the long term.
- Blue Hydrogen: Similar to grey hydrogen, blue hydrogen uses carbon capture and storage (CCS) to reduce CO2 emissions. While better than grey, it still relies on natural gas.
- Green Hydrogen: Created through water electrolysis using renewable electricity, green hydrogen is the cleanest form, with no emissions. It is expected to become the leading production method in the future.
Transitioning to green hydrogen is crucial for climate goals, providing sustainable solutions for energy storage, transportation, and industry while supporting a low-carbon future.
Through Technology Scouting Services, Signicent ensures companies remain at the forefront of hydrogen advancements, discovering transformative innovations that fuel sustainable automotive technologies.
Why Green Hydrogen is the most preferred
Green hydrogen is gaining preference as a fuel for automotive over other alternatives like CNG and electric vehicles (EVs). But why is this the case? Hydrogen offers several advantages:
High Energy Density: Hydrogen has a higher energy density compared to batteries, making it suitable for long-range and heavy-duty vehicles.
Fast Refueling: Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs) can be refueled in minutes, similar to conventional gasoline vehicles, unlike EVs which require longer charging times.
Efficiency and Range: Hydrogen vehicles outperform traditional battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) in range, with fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) achieving up to 400-500 miles per tank. This advantage makes them ideal for long-haul transport and heavy-duty applications.
Environmental Benefits: Green hydrogen-powered vehicles emit only water vapor, aligning with global decarbonization goals and combating climate change.
Heavy Transport Applications: Hydrogen’s energy density makes it particularly suitable for trucks, buses, and trains, addressing limitations faced by electric batteries in these domains.
Challenges Associated with Current Systems: EVs, CNG, and Fossil Fuels
While electric vehicles (EVs), compressed natural gas (CNG), and other alternatives to fossil fuels are improving, they still face challenges that hinder their wide adoption:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs):
Battery Production and Disposal: EVs rely on lithium-ion batteries, which require minerals that are rare and difficult to mine, leading to environmental concerns. The recycling of EV batteries is also an ongoing challenge.
Range and Charging Infrastructure: EVs currently have limitations on driving range and require long charging times, making them less practical for long trips compared to gasoline vehicles.
- CNG and Methane Fuels:
While CNG is cleaner than gasoline, it still relies on natural gas, a fossil fuel. Methane leaks during extraction and transportation contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, undermining its environmental benefits.
- Fossil Fuels:
The continued reliance on fossil fuels for energy generation contributes to the depletion of natural resources and is the leading cause of climate change. Reducing dependence on fossil fuels is crucial for achieving sustainability.
As such, the adoption of green hydrogen, which is free from these limitations, is seen as a critical step toward achieving a sustainable, low-carbon future.
Signicent’s Technology Scouting identifies emerging hydrogen solutions, enabling businesses to adopt advanced technologies like fuel cell innovations, electrolyzer designs, and storage methods.
Emerging Innovations in Green Hydrogen Technology
The development of green hydrogen technologies is accelerating, and several innovations are driving its potential:
Electrolyzer Advancements: Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) electrolyzers have become more efficient, reducing energy consumption per kilogram of hydrogen produced. Companies like ITM Power, Nel ASA, and Cummins are at the forefront of developing more efficient PEM electrolyzers. New models, like Newtrace’s electrolyzer, are pushing costs down and enhancing scalability.
Symbion Cell Technology: A joint venture between Faurecia and Michelin, Symbio’s fuel cells convert hydrogen and oxygen into electricity. This technology drives the adoption of zero-emission hydrogen mobility solutions, supporting the transition to sustainable transportation by offering a cost-effective and efficient way to power vehicles.
This innovation simplifies hydrogen systems by removing membranes, enhancing durability, and operating at 300°C, ensuring high efficiency. It accelerates sustainable transportation with cost-effective, clean hydrogen mobility solutions for a greener future.
Ammonia-Based Hydrogen Extraction: Using cesium dihydrogen phosphate as an electrolyte, this method extracts hydrogen from ammonia, enabling high-capacity, cost-effective transportation through existing pipelines. Ammonia is also abundant and non-toxic.
Hydrogen Storage Solutions
Innovations like metal hydrides and Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers (LOHCs) offer high energy density storage, making it easier and more efficient to store hydrogen. Companies like Hydrogenious Technologies and Honeywell are leading in this space.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Continuous advancements in fuel cell technology by companies like Ballard Power Systems have improved efficiency. Fuel cells which convert hydrogen into electricity with water vapor as the only byproduct, have improved efficiency and are now widely applied in clean transportation like hydrogen-powered vehicles, buses, and trucks.
- Sustainable Materials: The use of biopolymers such as cellulose and carbon-based components in electrolyzers and fuel cells is helping reduce the environmental impact of green hydrogen production. Companies like DuPont are enhancing performance while being more sustainable and more over these materials enhance performance while being more sustainable.
These innovations collectively enhance the accessibility, affordability, and scalability of green hydrogen, driving it toward widespread use in the transition to a low-carbon economy.
With Technology Gap Analysis, Signicent identifies untapped opportunities in hydrogen technology, enabling businesses to bridge gaps and stay ahead in the race toward a green automotive future.
Benefits and Future Impact
Green hydrogen offers numerous benefits and has the potential to significantly impact the future:
- Environmental Benefits: Green hydrogen produces zero emissions, making it a key player in reducing global carbon footprints.
- Economic Benefits: The green hydrogen market is expected to grow significantly, creating jobs and boosting economies.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in electrolysis and hydrogen storage are making green hydrogen more viable and cost-effective.
Signicent accelerates hydrogen-related chemical innovations through Chemical Structure Search, offering insights into unique formulations and ensuring compliance with existing patents.
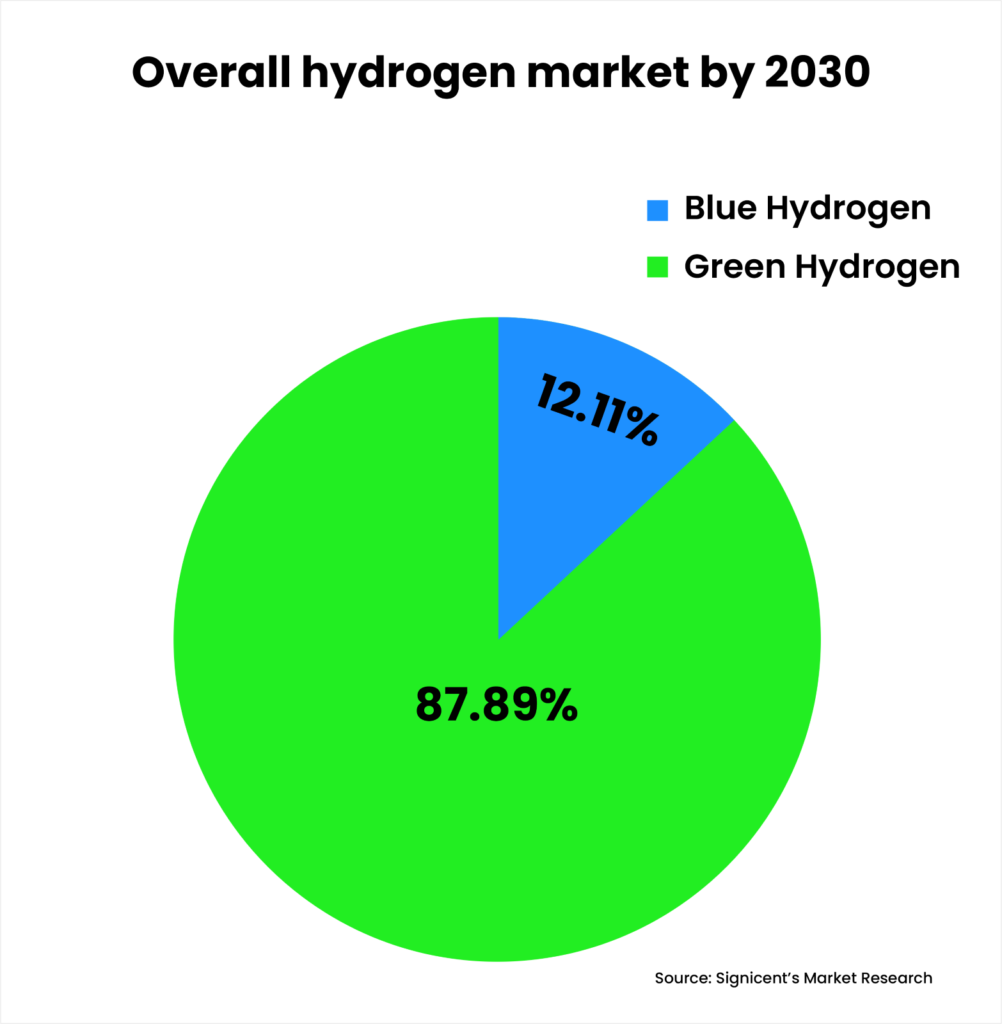
Market Outlook for Green and Blue Hydrogen
The global market for green hydrogen is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of more than 50% over the next decade. This growth is driven by increasing investments in renewable energy, the need for decarbonization, and the declining cost of hydrogen production technologies. By 2030, the green hydrogen market is projected to reach USD 100 billion globally.
- Green Hydrogen Market Outlook: The green hydrogen market is currently concentrated in Europe, which leads in the development of hydrogen infrastructure. However, other regions like Asia-Pacific and North America are catching up, with China and the U.S. increasing their investments in hydrogen production and infrastructure.
- Blue Hydrogen Market Outlook: Blue hydrogen is also gaining traction, particularly in regions where natural gas is abundant. It is seen as a transitionary solution to green hydrogen, offering a pathway to decarbonization without relying on renewable energy sources alone.
Signicent’s Market Assessment and Valuation services provide in-depth projections for green hydrogen demand, assisting businesses in evaluating opportunities and planning strategic investments.
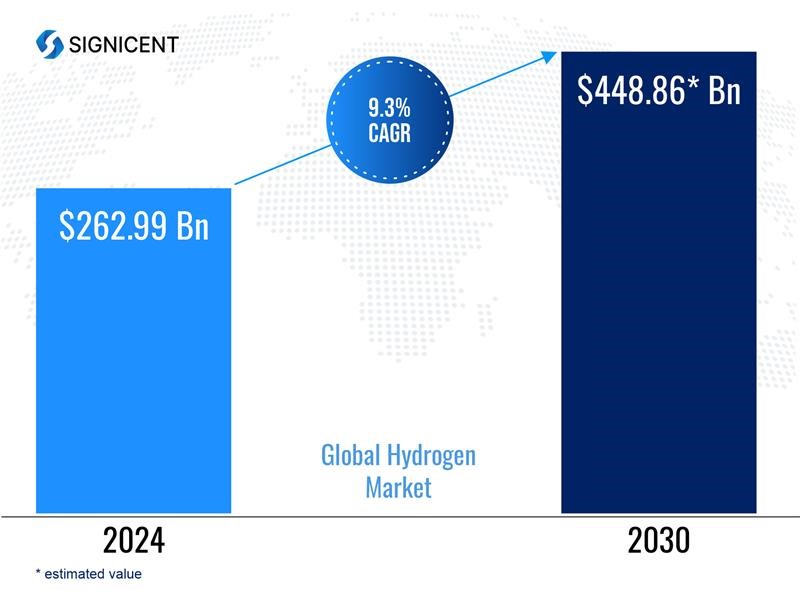
According to a report by Signicent’s Market Research the Global Hydrogen Market size is likely to reach values in the ranges shown below.
Recent Mergers and Acquisitions in the Green Hydrogen Market (2024)
The green hydrogen market has seen significant mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activity in 2024, reflecting the growing importance of hydrogen in the global energy transition. Here are some notable recent M&A deals involving top companies:
- Mitsubishi HC Capital and European Energy: In Q1 2024, Mitsubishi HC Capital acquired a minority stake in European Energy for $761.5 million. This deal highlights the strategic importance of green hydrogen projects in Europe.
- Fusion Fuel and Quality Industrial Corp: Fusion Fuel announced the completion of its acquisition of Quality Industrial Corp. (QIND) in November 2024. This strategic move aims to enhance Fusion Fuel’s capabilities in green hydrogen production and align with its long-term vision.
Emerging key players in spotlight from Europe
Here are the top 5 key players in the European green hydrogen market:
Key players in the green hydrogen market from the automotive sector

Signicent’s Contributions to the Green Hydrogen Market
Signicent plays a vital role in providing insights and analysis for companies involved in green hydrogen. Through market research, technology scouting, and patent landscape analysis, Signicent helps businesses identify emerging trends and technologies that could drive the future of green hydrogen.
Conclusion: The Future of Green Hydrogen
As the world accelerates its efforts to transition to renewable energy, green hydrogen is poised to play a critical role in the global energy mix. With advancements in technology, decreasing costs, and increasing investments, green hydrogen is expected to become a cornerstone of future energy systems. Its ability to decarbonize heavy industries, store renewable energy, and power transportation makes it an indispensable element of the fight against climate change. By the mid-21st century, green hydrogen could be the fuel that powers a sustainable, low-carbon world.
About Signicent LLP
We assist businesses globally in their technology innovations, R&D, new product development, patents, valuation, product commercialization & market research needs.
Services Offered:
- Patent Landscape
- Patent Portfolio Analysis
- Patent Invalidity Search
- Patent Licensing Services
- Freedom to operate (FTO)
- Chemical Structure Search
- Design Patent Search
- Technology Scouting
- Technology Landscape Analysis
- Technology gap analysis
- Technology Intelligence
- Market Research
- Bio Sequence Search
- Manufacturers Search/ Supplier search
Elevate your Innovation and Research with Signicent’s cutting edge approach to assist you with Technology and Market related matters alongside the IP aspect of the analysis.


