Introduction
When people hear the phrase EU regulations, it often sounds complex, rigid, or even intimidating. In reality, EU regulation is not a single rulebook or a fixed checklist—it is a dynamic system that evolves with society, technology, and global challenges. Its primary purpose is simple: to protect people, ensure fair competition, and safeguard the environment, while allowing businesses to operate smoothly across borders.
At the root of this system is the European Union, which creates uniform protocols so products, services, and data can move freely across member states without compromising safety, ethics, or transparency. Whether it’s a cosmetic cream, packaged food, medical product, or digital service, EU regulations ensure that what reaches consumers meets shared standards of quality and responsibility.
Today, EU regulation is no longer about ticking approval boxes. It focuses on accountability across the entire product lifecycle—from sourcing raw materials and manufacturing processes to labeling, data usage, distribution, and even end-of-life disposal.This shift reflects a broader change, with regulation becoming proactive, preventive, and sustainability driven, aligning with current and future analysis.
Why EU Regulations Matter (More Than Ever)
The European Union has positioned itself as a global benchmark for regulation. If a product is compliant with EU standards, it is often viewed as trustworthy in international markets as well. This global influence is not accidental—it is driven by growing consumer expectations and global risks.
Several forces are shaping this regulatory importance. Consumers today are more informed and vocal about what they use, eat, and share online. Climate change has pushed governments to enforce environmental responsibility. Rapid digitalization has raised serious concerns about privacy and data misuse. At the same time, past safety incidents across industries have reinforced the need for stricter oversight of chemicals, materials, and health-related products.
As a result, EU regulations now act as a filter. They reward businesses that are transparent, responsible, and future-ready, while limiting shortcuts that may harm people or the planet. For companies, compliance is no longer just about avoiding penalties, it is about earning long-term trust and market credibility.

Where EU Regulatory Focus Is Strongest: Key Industries Under the Lens
EU regulators do not treat all industries the same, with scrutiny guided by technology roadmaps and their direct impact on human health, safety, and the environment.
Cosmetics & Personal Care
These products come into direct contact with the human body, making ingredient safety, labeling accuracy, and allergen control critical. Claims such as “natural,” “organic,” or “dermatologically tested” are closely monitored to prevent misleading communication.
Food & Beverages
Food regulations focus on consumer safety, nutritional transparency, contamination control, and traceability. From ingredient sourcing to shelf labeling, every stage is regulated to ensure public health and informed choices.
Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare
This is one of the most tightly regulated sectors. Safety, clinical evidence, manufacturing standards, and post-market surveillance are all mandatory. Even packaging, storage conditions, and patient information leaflets are regulated.
Chemicals & Manufacturing
Industries using raw chemicals, intermediates, or industrial substances face strict obligations related to toxicity, environmental impact, and worker safety.
Digital, AI & Data-Driven Businesses
With growing digital dependence, data protection, cybersecurity, and ethical data usage are now central regulatory priorities.

How EU Regulations Impact Real Businesses
EU regulations reshape how businesses design products, manage operations, and compete globally, turning compliance into a strategic driver rather than an administrative burden.
- Cosmetics brands reformulate products, remove restricted ingredients, perform safety assessments, maintain product information files, and continuously monitor EU regulatory updates changes compliance.
- Food businesses ensure ingredient traceability, hygiene compliance, accurate nutrition and allergen labeling, reducing recall risks, protecting consumers, and preserving long-term brand trust.
- Pharmaceutical companies manage longer approvals, clinical validations, strict manufacturing audits, higher costs, but achieve stronger patient safety, regulatory confidence, and market credibility.
- Across industries, EU regulations demand documentation, transparent supply chains, sustainability integration, internal controls, and continuous compliance management aligned with evolving regulatory expectations.
- Although strict compliance generates greater brand positioning, improved risk management, customer trust, operational resilience, and smoother access to global and European markets.
Supply Chain Accountability & Traceability Obligations
One of the most critical shifts in EU regulation is the growing focus on supply chain accountability. Compliance no longer ends at a company’s factory gate. Businesses are increasingly responsible for what happens upstream and downstream, with supply chain analysis covering raw materials, distribution, use, and disposal.
EU regulations now expect companies to know where their materials come from, how they are processed, and whether suppliers follow ethical, environmental, and safety standards. This is especially relevant for industries such as cosmetics, food, pharmaceuticals, and electronics, where ingredient sourcing, contamination risks, and labor practices directly affect consumer safety.
Traceability systems, supplier audits, and transparent documentation are becoming standard expectations. Digital tools and batch-level tracking are also gaining importance, enabling faster responses during recalls or investigations. In this regulatory environment, supply chains are no longer invisible—they are part of the product’s compliance identity.
Key Regulatory Frameworks Shaping Industries
Instead of listing laws in isolation, it is more useful to understand what problem each framework is designed to solve.
1. Product Safety & Chemicals
Chemical safety is a cornerstone of EU regulation. Frameworks such as REACH and CLP ensure that substances used in products do not harm human health or the environment. The responsibility lies with companies to prove safety before placing products on the market. This reverses the traditional approach where risks were addressed only after damage occurred.
2. Sustainability & Environment
Environmental regulations are driving one of the biggest transformations across industries. The EU promotes carbon reduction, circular economy models, eco-design principles, and waste minimization. Products are increasingly evaluated not only on performance but also on environmental footprints. Sustainability compliance is no longer optional—it has become a competitive differentiator.
3. Consumer Transparency & Labeling
EU regulations strongly protect consumers from misleading information. Whether it is ingredient lists, origin claims, or environmental promises, transparency is mandatory. From cosmetics and food to electronics, brands must support every claim with evidence. Greenwashing is actively monitored, and penalties are rising. In the EU, trust is regulated.
4. Data & Digital Compliance
With General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the EU made privacy a fundamental right. Any organization handling EU user data—regardless of location—must follow strict rules on consent, storage, access, and breach reporting. This regulation reshaped global digital practices and forced businesses to rethink how they collect and use data.
Pre-Market Approval vs. Post-Market Monitoring
| Factor | Pre-Market Approval | Post-Market Monitoring |
| Primary objective | Ensure product safety, quality, and legal compliance before entering the EU market. | Ensure ongoing safety, performance, and compliance after products reach real consumers. |
| Key activities | Safety assessments, technical documentation, risk analysis, and regulatory submissions before market launch. | Performance monitoring, consumer feedback collection, adverse event reporting, and corrective actions. |
| Industries most impacted | Pharmaceuticals, medical devices, chemicals, cosmetics, and other high-risk regulated product categories. | All regulated industries, especially consumer-facing products with continuous real-world usage. |
| Regulatory focus | Prevent risks early by evaluating product design, formulation, and intended use. | Detect emerging risks during market use and manage issues through corrective measures. |
| Business responsibility | Demonstrate readiness, meet legal requirements, and obtain approval prior to commercialization. | Maintain compliance, report issues, update authorities, and manage products throughout their lifecycle. |
What’s Changing Right Now?
This is where EU regulation is evolving fast, and where many businesses fall behind.
The regulatory system is shifting from a reactive model to a preventive one. Instead of responding after harm occurs, regulators now aim to prevent risks before products reach the market.
This includes stricter pre-market assessments, meaning more documentation and testing before launch. Digital product passports are being introduced to improve traceability and lifecycle transparency. Sustainability reporting is becoming mandatory, requiring companies to disclose environmental and social impact data. Audits are increasing, and loopholes are closing.
For businesses, this means compliance is no longer a one-time task. It is an ongoing process that must be embedded into product design, sourcing decisions, and corporate strategy.
Impact of Non-Compliance: Penalties, Recalls & Market Bans
Non-compliance with EU regulations carries serious consequences that go beyond financial penalties. Depending on the severity of the issue, companies may face forced product recalls, temporary or permanent market bans, public safety warnings, and long-term reputational damage.
For consumer-facing industries, recalls can quickly erode trust and disrupt supply chains. In regulated sectors like food and pharmaceuticals, non-compliance may also trigger inspections, license suspensions, or legal action.
The EU’s enforcement mechanisms are becoming more coordinated across member states, reducing the ability to shift non-compliant products between markets. As transparency increases, regulatory actions are also more visible to the public. This makes compliance not just a legal necessity, but a core component of brand credibility and business resilience.
What Companies Must Do to Stay Compliant
To succeed in the EU market, companies must move beyond reactive compliance by adopting a structured, proactive approach supported by continuous regulatory monitoring.
First, regulatory awareness must be built into decision-making. Teams should track updates, understand sector-specific requirements, and assess how changes impact products early in development.
Second, documentation and traceability are critical. From raw materials to finished goods, every step should be recorded, validated, and accessible for audits.
Third, sustainability and safety should be integrated into innovation. Reformulating products, redesigning packaging, or adopting cleaner processes early reduces long-term compliance risks.
Finally, collaboration matters. Working with regulatory experts, testing labs, and compliance partners helps businesses stay aligned with evolving standards and avoid costly setbacks.
Innovation vs. Regulation: Finding the Right Balance
| Factor | Innovation Perspective | Regulatory Perspective |
| Core purpose | Drives new products, technologies, processes, and competitive differentiation. | Ensures safety, sustainability, transparency, and responsible market practices. |
| Primary focus | Improving performance, efficiency, sustainability, and customer value. | Protecting consumers, environment, and market integrity. |
| Key challenge | Innovating quickly while managing regulatory and compliance constraints. | Guiding innovation without restricting technological advancement. |
| Early integration | Early compliance reduces redesign, delays, and market entry risks. | Early alignment enables smoother approvals and regulatory confidence. |
| Long-term outcome | Sustainable growth, differentiation, and faster global market access. | Trust, accountability, and long-term industry stability. |
Market Perspective: How EU Regulations Shape Market Access and Growth
The European market is rapidly advancing toward regulation-driven, sustainable product ecosystems, fueled by stricter compliance frameworks, green transition policies, and cross-border market harmonization.
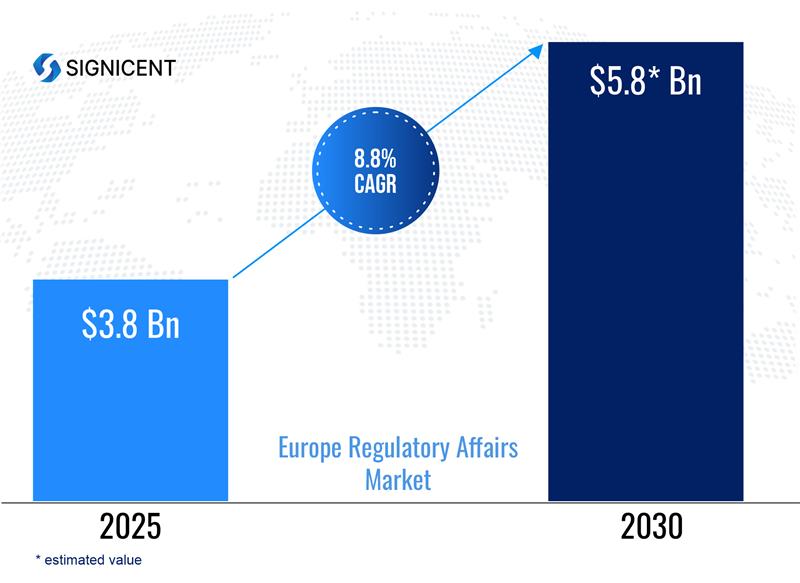
According to Signicent Market Research, EU compliance-driven industries are projected to grow from USD 3.5 Bn in 2024 to USD 5.8 Bn by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 7.5% (2025–2030), supported by increasing regulatory enforcement, sustainability mandates, and innovation-led compliance adoption.
Future Outlook: Where EU Regulation Is Headed Next
Looking ahead, EU regulation is expected to become even more forward-looking, data-driven, and sustainability-focused. Digital product passports, expanded ESG reporting, and stronger climate-related requirements are likely to become standard across industries.
Artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and advanced materials will also receive increased regulatory attention as their use expands. Rather than reacting after risks emerge, the EU aims to anticipate challenges and set guardrails early.
For businesses, the future regulatory landscape will reward adaptability, transparency, and long-term thinking. Companies that align compliance with strategy will not only meet legal requirements but also strengthen trust, resilience, and global competitiveness.
FAQ’s on EU Regulations
1. What are EU regulations and why do they matter?
EU regulations set common rules to protect consumers, ensure product safety, and enable fair trade across European markets.
2. Do EU regulations apply to non-EU companies?
Yes. Any company selling products or services in the EU must comply, regardless of where it is based.
3. Which industries are most affected by EU regulations?
Cosmetics, food, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, medical devices, and digital services face the highest regulatory scrutiny.
4. Is EU compliance a one-time process?
No. Compliance is ongoing and requires continuous monitoring, documentation, and updates throughout a product’s lifecycle.
5. How can businesses stay compliant with changing EU regulations?
By tracking regulatory updates, strengthening documentation, ensuring supply-chain transparency, and integrating compliance early into product development.


